Gastric function screening series
Classification:
Quantum dot platform
Key words:
Tel:
Product Details
|
Product status |
Blue ocean product |
|
Product status |
It will be approved for listing in September 2022. |
|
Product value |
PGⅠ/Ⅱ\G17 serological joint detection, the level changes of each index reflect the gastric mucosal atrophy site, and effectively distinguish the types of gastric atrophy. |
|
Product Category |
Gastric function screening, immunodiagnosis |
|
Features |
Rapid detection, combined indicators, quantitative analysis |
|
Market demand |
Smoking, heavy drinking, staying up late, irregular diet, chronic atrophic gastritis, gastric ulcer, gastric polyps and other gastric diseases in the past, HP infection and other people are the screening objects. In 2017, the Chinese Anti-Cancer Association promulgated the "Expert Consensus Opinions on Early Gastric Cancer Screening Process in China (Draft)", recommending regular gastric cancer screening for people over 40 years old. Early detection can more effectively control or cure gastric cancer. |
|
Market capacity |
Due to the improvement of people's living standards and health awareness, the market size of gastric cancer screening in China shows a trend of continuous growth. Its market size increased from 1.1 billion yuan in 2016 to 2.4 billion yuan in 2020, with a compound annual growth rate of 21.3% from 2016 to 2020. It is estimated that the gastric cancer screening market will reach 2.9 billion yuan in 2021. |
|
Core Technology |
Quantum dot immune technology, combined with quantitative detection technology |
|
Competitive Advantage |
Quantum dot detection is fast, sensitive and accurate; The joint detection is more comprehensive, and three indicators can be tested in one sampling test; It can quantitatively analyze the content of indicators, so that doctors can have a clearer control over the degree of risk and take targeted measures; Supporting a variety of testing instruments to meet the different needs of medical institutions at all levels. |
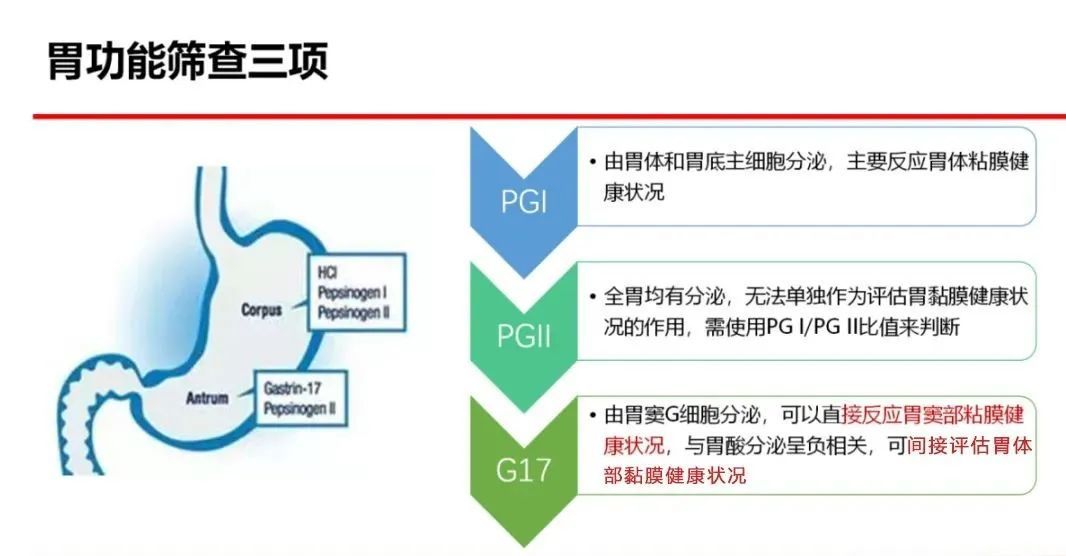
Introduction to three gastric functions
Pepsinogen (PG) is the precursor of pepsin, which is divided into pepsinogen I and pepsinogen II according to its biochemical and immunochemical properties.
Pepsinogen I is secreted by the chief cells of the fundic glands and the cervical mucus cells;
Pepsinogen II is secreted by fundic glands, cardia glands, pyloric glands, and duodenal glands.
The level of serum pepsinogen can reflect the secretion of pepsin and the state and function of gastric mucosa. When the gastric mucosa is lesioned, the content of pepsinogen in serum also changes.
Gastrin (G-17) is a gastrointestinal hormone mainly secreted by G cells in the gastric antrum and duodenum, which plays an important role in regulating the function of the digestive tract and maintaining its structural integrity.
G-17 is only secreted by G cells in the gastric antrum, so G-17 is an important indicator of gastric mucosal damage. If gastrin 17 is high, it may affect the digestion and absorption function of the stomach, leading to gastrointestinal diseases, such as gastritis, gastric ulcer and so on.
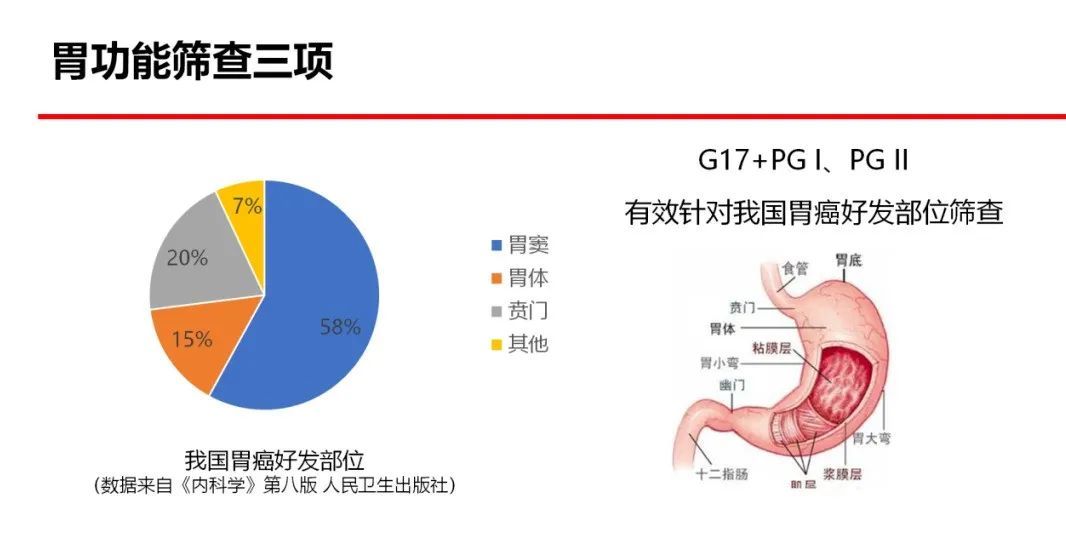
Gastroscopy combined with gastric mucosal biopsy is currently the gold standard for the diagnosis of gastric cancer, but the examination is invasive and not suitable for general screening and screening. The three non-invasive tests of gastric function can realize "serological" biopsy of gastric mucosa, and make further judgments on the health of the stomach. Superficial gastritis, erosive gastritis, gastric ulcer, duodenal ulcer, atrophic gastritis, gastric cancer, etc. High-risk groups were screened out. It is a simple, rapid, reproducible, non-invasive, and dynamic detection method that is very suitable for early screening of gastric cancer.
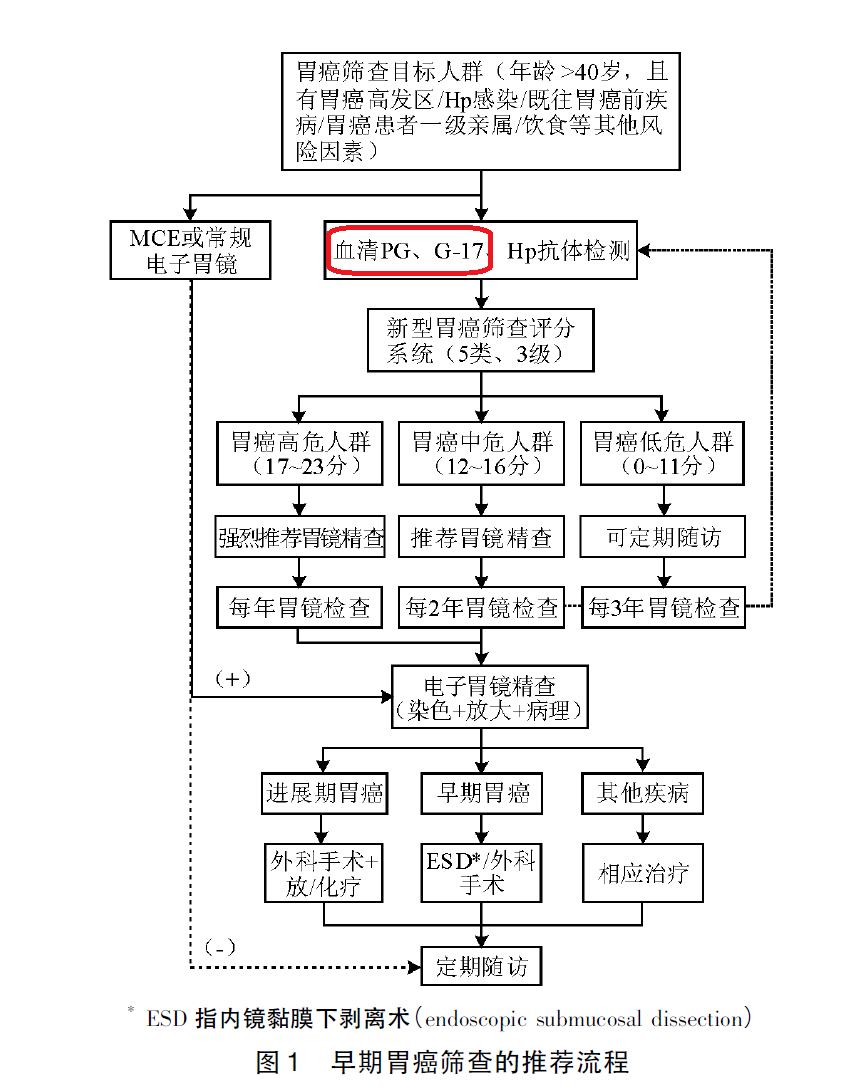
Clinical Application and Interpretation
|
Clinical application |
Content |
|
Early Screening |
Stomach health screening for high-risk groups; Stomach cancer screening. |
|
Auxiliary diagnosis, monitor |
Auxiliary diagnosis of gastroesophageal reflux disease; Dynamic monitoring of gastric mucosa to assist in judging the degree of gastric mucosal atrophy; Assist in judging the healing of peptic ulcer; Auxiliary evaluation of the efficacy of Helicobacter pylori Hp eradication therapy. |
|
Prognosis |
Auxiliary in judging the recurrence of peptic ulcer and gastric cancer after surgery. |
Interpret
| 1 |
PG: PG I ≤ 70 ng/mL and PG I/PG II ≤ 3: Gastric mucosal cells atrophy, it is recommended to do gastroscopy for further examination. Possible reasons: Atrophic gastritis is the majority, and special attention should be paid to high-risk factors such as atrophic gastritis, intestinal metaplasia, dysplasia, and gastric cancer. PG I ≤ 70 ng/mL and PG I/PG II > 3: Pepsin secretion is less, it is recommended to review regularly. Possible reasons: most of them have low gastric acid secretion, and there is a high risk of atrophic gastritis and intestinal metaplasia. PG I > 240ng/mL or PG II > 20ng/mL: If the gastric mucosa is damaged, it is recommended to do further examination by gastroscopy or abstinence from alcohol, and reexamination after two weeks. Possible reasons: PG II is relatively stable, but the active PGI will increase significantly when the gastric mucosa is attacked or damaged. HP infection, superficial gastritis, erosive gastritis, gastric ulcer, and duodenal ulcer can all increase serum PG I and PG II. Recurrent gastric ulcer PG II increased significantly, and duodenal ulcer recurrent PG I and PG II increased significantly. |
| 2 |
G-17: G-17≤1pmol/L: It indicates the risk of severe antrum atrophy or high acidity; G-17≥15pmol/L: It indicates the risk of gastric body mucosal atrophy or gastric antrum hyperplasia (need to rule out the influence of drugs such as PPI); G-17 at 7~15pmol/L: It indicates non-atrophic gastritis. Influencing factors of gastrin 17 detection: ① Diabetic patients should regularly monitor G-17 to prevent diabetic autonomic neuropathy. ② After taking PPI drugs, the level of G-17 usually increases significantly. If the increase of G-17 is not obvious, there is a risk of gastric atrophy. |
Guidelines/Consensus
It is precisely because of the important role of these three items that the detection of gastric diseases is recommended by many consensus documents, as follows.
| Guidelines/Consensus | Content |
| Article 16 of the 2008 Asia-Pacific Consensus on Gastric Cancer Prevention |
Low serum PG I level and low PG I/PG II ratio can be used as markers to identify high-risk groups for gastric cancer. |
| In 2014, the first domestic medical examination industry "quasi-standard" - "Expert Consensus on Basic Health Examination Items" | It is recommended that people with a history of gastric ulcers, gastric polyps, abdominal pain, diarrhea, weight loss, and tarry stools can be tested for pepsinogen, gastrin-17, and Helicobacter pylori for gastric cancer risk screening. |
| "Consensus Opinions on Early Gastric Cancer Screening and Endoscopic Diagnosis and Treatment in China (2014) Changsha" | Combined detection of serum G-17, PG I, PG I/PGII ratio and HPylori antibody can increase the accuracy of evaluating the scope and degree of gastric mucosal atrophy. |
| "Consensus Opinions on Chronic Gastritis in China, (2017)" | The detection of serum pepsinogen PGI, PGII and gastrin-17 is helpful to judge the presence and degree of gastric mucosal atrophy. |
| "Guidelines for Early Gastric Cancer Screening in China" (2017) | Three gastric function tests combined with endoscopic precise examination can improve the diagnosis rate of gastric cancer. |
| In 2018, the National Health and Medical Commission's "Notice on Printing and Distributing 18 Tumor Diagnosis and Treatment Standards including Primary Lung Cancer" | Serum pepsinogen and serum gastrin 17 were used as the basis for gastric cancer screening. |
Department application and testing population
| Application department | Test population (those who meet any of the following items 1 and 2-6 are recommended to be screened) |
|
Gastroenterology Physical examination Medical center Endoscopy Center … |
1. Over 40 years old, male or female; 2. People in areas with a high incidence of gastric cancer; 3. H.Pylori infected persons; 4. People with precancerous diseases of the stomach, such as chronic atrophic gastritis, gastric ulcer, gastric polyps, remnant stomach after surgery, hypertrophic gastritis, pernicious anemia; 5. First-degree relatives of gastric cancer patients; 6. There are other high-risk factors for gastric cancer, such as high salt, pickled diet, smoking, heavy drinking, etc.). |
Product description
The three tests of gastric function are of positive significance for the assessment of gastric health status, identification of gastric inflammation, effective detection of high-risk groups of gastric cancer, and improvement of the early diagnosis and treatment rate of gastric cancer in my country, which has positive significance for the prevention and treatment of gastric diseases.
Anhui Huibang Bioengineering Co., Ltd.'s three gastric function detection schemes (G-17, PGI/PGII) are in line with the characteristics of gastric cancer in the Chinese population, and are effective for early and rapid screening of atrophic gastritis and gastric cancer. In addition, Huibang Biotech also has clinically commonly used inflammation series (CRP, SAA PCT, IL-6), vitamin deficiency (25-OH-VD), prenatal and postnatal care (AMH), preeclampsia prediction and monitoring reagents, etc. roll out.
Previous Page
Next Page
Recommended Products
Online consultation