Inflammatory infection series
Classification:
Quantum dot platform
Key words:
Tel:
Product Details
|
Product status |
Red sea products |
|
Product status |
It will be approved for listing in December 2022. |
|
Product value |
Respiratory tract infection, pneumonia, sepsis, etc. can be tested individually or combined |
|
Product Category |
Inflammatory infection detection, immunodiagnosis |
|
Features |
Rapid detection, combined detection, quantitative analysis |
|
Market demand |
In the diagnosis and management of neonatal sepsis, which occurs in 1 to 10 cases per 1000 live births; in the diagnosis and management of patients with bacterial fever, early recognition of bacterial infection is crucial for treatment. Both require early diagnosis and early treatment. |
|
Market capacity |
The overall scale of the diagnosis market in the field of infection in my country has continued to expand, from 10.94 billion yuan in 2015 to 19.4 billion yuan in 2019, with an average annual compound growth rate of 15.4%. It is expected that the average annual growth rate will remain at about 15% in the next five years. Among them, immunodiagnosis is the method with the highest proportion of the infection market, and its market size has increased from 7.35 billion yuan in 2015 to 11.10 billion yuan in 2019, with a compound annual growth rate of 10.8%. |
|
Core Technology |
Quantum dot immune technology, single detection or combined quantitative detection technology |
|
Competitive Advantage |
Quantum dot detection is fast, sensitive and accurate; Single inspection or combined inspection is more comprehensive, and one-time sampling can test 1-4 indicators; It can quantitatively analyze the content of indicators, so that doctors can have a clearer control over the degree of risk and take targeted measures; Supporting a variety of testing instruments to meet the different needs of medical institutions at all levels. |
Infectious disease is one of the most common clinical disease types. Due to the various routes of infection, the variety of pathogens, and the individual differences in symptoms and signs, if the diagnosis and treatment cannot be confirmed in time, serious consequences may occur. Therefore, how to make early diagnosis and (or) differential diagnosis of infectious diseases clinically is a practical problem to be solved urgently. When an infectious disease occurs, it is particularly important to first identify the type of infection in the patient.
The detection of the four items of inflammation (CRP/SAA/PCT/IL-6) helps to quickly and effectively identify the type of infection, which can not only alleviate the insufficient speed of diagnosis, but also classify the diagnosis, avoiding the abuse of antibiotics and the waste of scarce medical resources in critical periods.
Full scale C-reactive albumin (CRP)
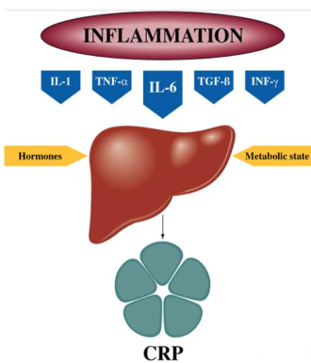
lCRP is an acute phase protein of infection synthesized by liver cells. CRP usually increases after bacterial infection, and the degree of increase is positively correlated with infection or severity, and the increase is not obvious after viral infection. Therefore, CRP is usually used as one of the reference indicators to identify bacterial or viral infections.
lCRP is significantly elevated within 6-12 hours of bacterial infection, and does not increase or is not significantly elevated during viral infection.
Clinical significance
Clinical application
1. Differentiate Bacterial and Viral Infections
2. Detection of inflammatory diseases and postoperative monitoring
3. Evaluation and management of antibiotic treatment effect
4. Cardiovascular disease risk and treatment assessment
| Project name | Test results | Clinical Application Recommendations |
| hsCRP or CRP | >10mg/L | Indicates the possibility of another infection (bacterial or viral) |
| 10mg/L-20mg/L | Suggesting viral infection or mild bacterial infection | |
| 20mg/L-50mg/L | suggestive of general bacterial infection | |
| >50mg/L | Suggesting a serious bacterial infection |
In the absence of inflammation, hsCRP serves as a risk index assessment indicator for cardiovascular disease:
| Project name | Test results | Clinical Application Recommendations |
| hsCRP | <1.0mg/L |
The risk of cardiovascular disease was assessed as low risk. Cardiovascular disease risk assessment is moderate risk, it is recommended to give anti-infection treatment of 1.0mg/L-3.0mg/L; re-test after 2 weeks, and take the average value as the basis of observation. |
| >3.0mg/L | Cardiovascular disease risk assessment is high risk, it is recommended to give anti-infection and antithrombotic treatment at the same time. |
Serum amyloid A (SAA)
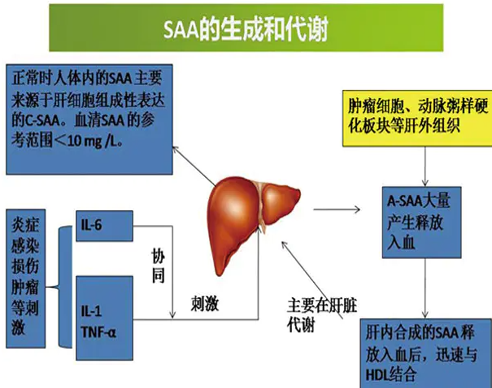
● SAA is a sensitive protein in the acute phase of infection. SAA is usually produced in large quantities after bacterial and viral infections. Compared with CRP, SAA has obvious advantages in increasing speed and magnitude.
● SAA starts to rise about 5-6 hours after the inflammatory response, and it rises significantly during virus infection, and after the pathogen is cleared, SAA quickly drops to the normal level.
Clinical significance
Clinical application
1. Signs of inflammation in infectious diseases
2. Independent indicators for predicting cardiovascular events
3. Indicators of transplant rejection
4. Indicators of amyloidosis
| SAA concentration (mg/L) | Clinical significance | Illustrate |
| <10 | / | • None. Essentially normal • Negative SAA has a high negative predictive value for neonatal sepsis |
| >10 | Differentiate between viral and bacterial infections |
• SAA is elevated in both viral and bacterial infections, while CRP is hardly or not significantly elevated in viral infections; SAA is more sensitive than CRP to weak inflammatory stimuli; • In the early stage of infectious diseases in children, it can effectively distinguish bacterial or viral infections because the signs and symptoms are less obvious. • If SAA persists between 10-100mg/L, it indicates a higher possibility of viral infection; if SAA persists >100mg/L, it indicates a greater possibility of acute bacterial infection. |
| kidney transplant rejection | • In the event of transplant rejection, the concentration of SAA increases, while the concentration of CRP changes little, which is one of the earliest indicators of increase, and serum SAA can be used as an indicator | |
| Amyloidosis | • Almost all patients with reactive amyloidosis maintain high levels of SAA for a long time. | |
| Tumors, coronary heart disease, etc. | • The levels of SAA in various tumor patients and heart disease patients are increased to varying degrees, and it has a certain relationship with the development of the disease. |
Interleukin-6 (IL-6)
● Interleukin 6 (IL-6) is an important member of the cytokine network and plays a central role in the acute inflammatory response. After the production of IL-6, it induces the production of C-reactive protein (CRP) and procalcitonin (PCT), and Inflammatory disease is directly related to the degree of infection. IL-6 can diagnose early inflammation and warn the occurrence of sepsis faster. In addition, the half-life of IL-6 is shorter than that of CRP and PCT, which can respond to the effect of antibiotic treatment more quickly.
● The relative advantage of L-6 detection lies in the early detection of acute infection, dynamic observation of IL-6 level is also helpful to understand the degree and progress of infectious diseases and judge the prognosis.
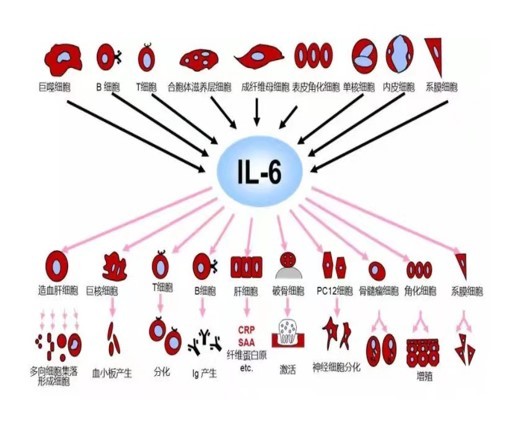
Clinical significance
Clinical application
1. Early warning of sepsis, early identification of critically ill patients.
2. Monitor the more sensitive early identification indicators of postoperative infection.
3. To guide the rational use of antibiotics.
4. Identify Gram-negative bacteria and positive bacteria.
| IL-6 concentration (pg/ml) | Clinical significance |
| <7 | None, basically normal |
| 7~150 | Indicates inflammation, mild infection |
| 150~250 | General bacterial infection or systemic inflammatory response likely |
| >250 | suggestive of sepsis |
| >1000 | Suggesting severe poor prognosis |
Procalcitonin (PCT)
● PCT is a glycoprotein with no hormone activity. The content of PCT in normal human serum is extremely low, and it rises rapidly during bacterial infection. The biological characteristics of PCT provide an important basis for the identification of different pathogenic infections, especially bacterial and viral infections.
● PCT is quickly released into the blood within 2-3 hours of bacterial infection. It is more sensitive to systemic infection and has a better correlation with infection and sepsis. The increase of its level is not affected by the immune suppression state of the body. Treatment monitoring is even more valuable. Dynamic detection of PCT serum level can monitor the disease and judge the prognosis.
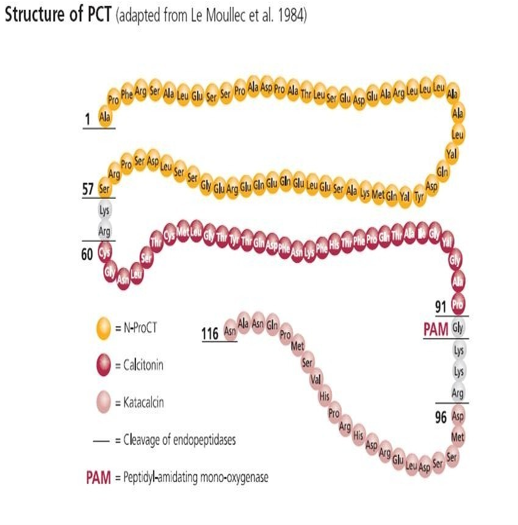
Clinical significance
Clinical application
1. Rapid differential diagnosis of bacterial/viral infection
2. Optimal detection index for bacterial infection/sepsis
3. The best markers for antibiotic application management
| PCT concentration (ng/ml) | Possible diseases | Antibiotic Use Recommendations |
| <0.05 | None, basically normal | Do not use |
| 0.05~0.5 | Mild or localized bacterial infection, tumor, hoof tissue disease | <0.25, not recommended, review PCT, >0.25, recommended |
| 0.5~2 | There is likely to be a systemic bacterial infection, but it should be noted that PCT increases in non-infectious conditions, such as surgery, surgical trauma, etc. | It is strongly recommended to use |
| 2-10 | systemic infection | |
| >10 | Severe sepsis, septic shock |
CRP, SAA, PCT, IL-6 concentration change trend chart
IL-6 plays a central role in the acute inflammatory response, and is the first to be produced when the body has tissue damage or infection, and has a high sensitivity.
SAA begins to rise about 5-6 hours after the inflammatory response, and rises significantly during virus infection. After the pathogen is cleared, SAA quickly drops to normal levels.
CRP is significantly elevated within 6-12 hours of bacterial infection, and does not increase or is not significantly elevated during viral infection.
PCT is quickly released into the blood within 2-3 hours of bacterial infection. It is more sensitive to systemic infection and has a better correlation with infection and sepsis. The increase of its level is not affected by the immune suppression state of the body. Monitoring is more valuable.
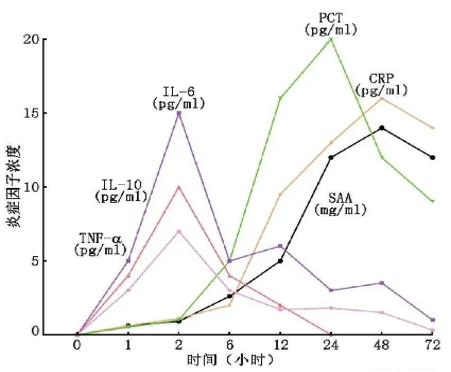
L-6 acute inflammation is the first to be produced, PCT bacterial infection is quickly released into the blood within 2-3 hours,
The inflammatory response of SAA began to increase after 5-6 hours, and the CRP bacterial infection increased significantly after 6-12 hours.
Joint detection of infection markers is more meaningful
● SAA is usually combined with CRP to identify bacterial and viral infections. When both SAA and CRP increase, it indicates the possibility of bacterial infection; when SAA increases but CRP does not increase, it indicates viral infection.
● PCT combined with IL-6 detection can complement each other, and the combined diagnostic value is higher. IL-6 can accurately assess prognosis, predict mortality, and is an "early warning" marker that rises rapidly after inflammation occurs; while PCT is a diagnostic marker with high sensitivity and high specificity. PCT combined with IL-6 can be used in the diagnosis and prognosis of sepsis
● The difference of IL-6 level in G-bacteria and G+ bacteria is greater than that in PCT. The combined detection of the two can better assist in the identification of G+/G- bacteria. If both PCT and IL-6 are significantly increased, the possibility of G-bacteria infection is high. If PCT is high but IL-6 is not obvious, the possibility of G+ bacteria should be considered.
Joint detection of infection markers is more meaningful
| CRP | WEATHER | PCT | IL-6 | |
| Clinical features | Elevated bacterial infection, 30% elevated viral infection | Significant increase in viral infection, significant increase in bacterial infection, and significant decrease in infection cure | Systemic severe bacterial infection, sepsis, monitoring of antibiotic use | Bacterial infection and viral infection, mycoplasma infection, malignant tumor, severe tissue damage, autoimmune disease, etc. |
| Critical value | 10.0mg/L; hsCRP is 3.0mg/L | 10.0mg/L | 0.5mg/L; 2.0mg/L suggests systemic bacterial infection | <7pg/mL is normal; 7-150pg/mL mild inflammation or infection; 150-250pg/mL general bacterial infection or systemic inflammatory response; >250pg/mL may suggest sepsis |
| Concentration change |
Rising period: 6-12h Platform period: 24-48h Half-life: 18h |
Ascent period: 8h Plateau period: 5-6h Half period: 50min |
Rising period: 2-4h Plateau period: 12-48h Half-term: 22-26h |
Rising period: 0-1h Plateau period: 2h Half-life: 50min |
| Systemic reaction | ↑↑ | ↑↑ | ↑↑ | ↑↑ |
| Local inflammation | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ |
| Bacterial infections | ↑↑ | ↑↑ | ↑↑ | ↑↑ |
| Viral infection | - | ↑↑ | - | ↑↑ |
| fungal infection | - | - | ↑ | ↑↑ |
Product display

Testing method
CRP/SAA
Take 10uL of serum/plasma (15uL for whole blood sample), add it to the sample buffer, mix well and draw 80uL, add it to the sample hole of the test card, time it for 5min, and use the supporting instrument for detection
PCT/IL-6
Add 80uL of serum/plasma or 120uL of whole blood into the sample hole of the test card, time it for 15 minutes, and use the matching instrument for detection
Inspection requirements
• The sample types that this kit is suitable for are human serum, plasma or whole blood samples.
• Avoid samples that are hemolyzed, icteric, hyperlipidemic, or visibly contaminated with microorganisms.
• After sample collection, the IL-6 test must be completed within 8 hours, the PCT/SAA test must be completed within 2 hours, and the CRP test must be completed within 4 hours. If the test cannot be carried out on time, please refer to the instructions for storage methods.
• EDTA-K2 anticoagulant is recommended for plasma and whole blood samples.
Features
▲ Fluorescent quantum dot platform, high sensitivity, stable performance, true and reliable signal
▲ The test can not only achieve single-person sample inspection at any time, but also meet the needs of large-scale batch rapid detection
▲ Variety of sample choices, including serum, plasma, and whole blood
▲ Single card detection, convenient combination, CRP/SAA detection results in 5 minutes, PCT/IL-6 detection results in 15 minutes
▲ Test items:
Inflammatory markers: CRP, PCT, SAA, IL-6
Tumor markers: PGⅠ, PGⅡ, G-17
Vitamin detection: 25-OH-VD
▲ Applicable departments: Laboratory, Emergency, ICU, Pediatrics, Respiratory, Surgery, Hematology, Oncology, Cardiology, etc.
Previous Page
Next Page
Recommended Products
Online consultation